|
Polymer Composites
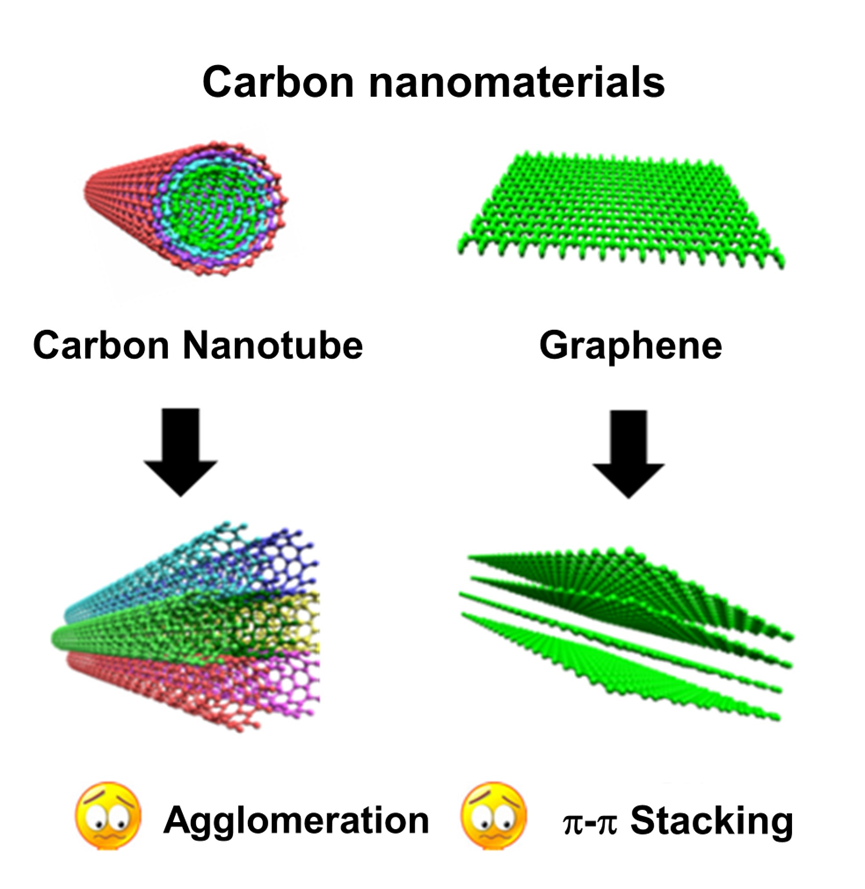
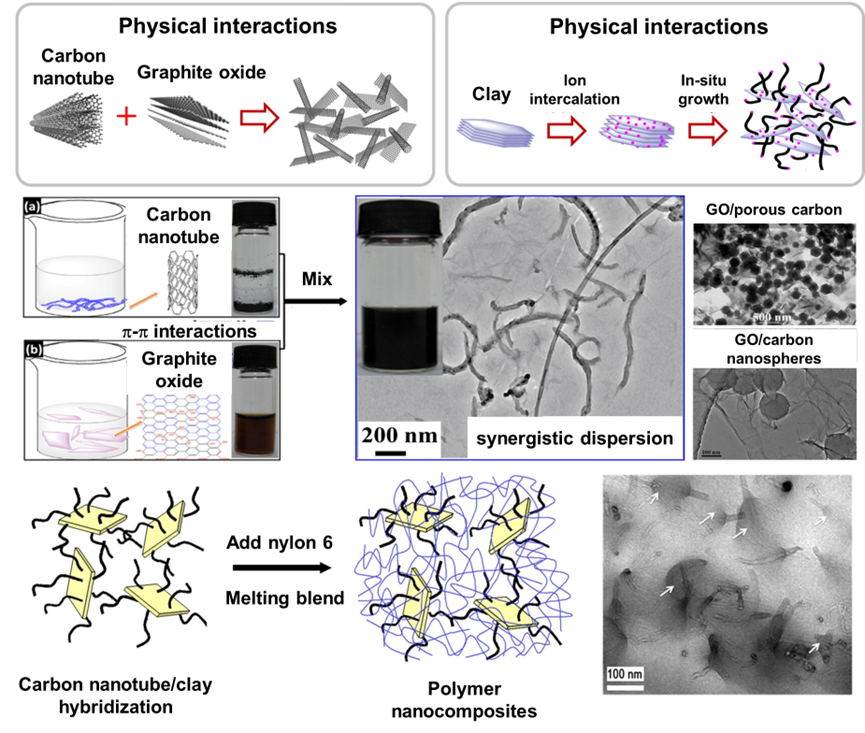
Polymer Composites How to solve the problems of nanoparticle agglomeration in polymer matrix and weak interfacial interactions between nanoparticles and polymer matrix has been a key challenge in the field of polymer-based composites. Our group proposes a nanoparticle hybridization strategy to successfully achieve efficient compounding and synergistic dispersion between heterogeneous and heterophase nanoparticles with different dimensions and properties. The compounding of nanoparticles with polymer matrix to achieve uniform dispersion of nanoparticles in polymer matrix and strong interfacial interaction between nanoparticles and matrix is obtained, thus solving the bottleneck problems of agglomeration and weak interfacial interaction of nanoparticles in polymer matrix. This study solves the bottleneck problems such as agglomeration and weak interface of nanoparticles in polymer matrix, and realizes the high-performance and multi-functionalization of polymer matrix. 1. Efficient hybridization construction of nanoparticles
To address the key problems of easy agglomeration and weak interfacial interactions of nanoparticles in polymer matrix, our group proposes a new method for efficient hybridization of nanoparticles with different dimensions and/or properties, revealing the synergistic dispersion mechanism of polymer composites and achieving the high-performance and multi-functionality of polymer composites.
2. Synergistic dispersion of nanoparticles in polymer matrix
To address the key issues of weak interfacial interaction between nanoparticles and polymer matrix in polymer composites, our group proposes a new idea of hybridization construction and controlled assembly of nanoparticles to regulate the interfacial interactions of composites, thereby obtaining unique polymer composites with largely enhanced interfacial interactions as well as integrated performances and functions.
Representative publications: 1. Y. Wang, Y. Liu, R. Plamthottam, M. Tebyetekerwa, J. Xu, J. Zhu, C. Zhang*, T. X. Liu*. Highly stretchable and reconfigurable ionogels with unprecedented thermoplasticity and ultrafast self-healability enabled by gradient-responsive networks. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 3832. 2. B. Zhang, X. Zhang, K. Wan, J. Zhu, J. Xu, C. Zhang*, T. X. Liu*. Dense hydrogen-bonding network boosts ionic conductive hydrogels with extremely high toughness, rapid self-recovery and autonomous adhesion for human-motion detection. Research 2021, 2021, 9761625. 3. A. Wang, Y. Wang, B. Zhang, K. Wan, J. Zhu, J. Xu, C. Zhang*, T. X. Liu*. Hydrogen-bonded network enables semi-interpenetrating ionic conductive hydrogels with high stretchability and excellent fatigue resistance for capacitive/resistive bimodal sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128506. 4. Y. Wang, M. Tebyetekerwa, Y. Liu, M. Wang, J. Zhu, J. Xu, C. Zhang*, T. X. Liu*. Extremely stretchable and healable ionic conductive hydrogels fabricated by surface competitive coordination for human-motion detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127637. 5. H. Song, Y. Sun, J. Zhu, J. Xu, C. Zhang*, T. X. Liu*. Hydrogen-bonded network enables polyelectrolyte complex hydrogels with high stretchability, excellent fatigue resistance and self-healability for human motion detection. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 217, 108901. 6. L. Li, Y. Zhang, H. Lu, Y. Wang, J. Xu, J. Zhu, C. Zhang*, T. X. Liu*. Cryopolymerization enables anisotropic polyaniline hybrid hydrogels with superelasticity and highly deformation-tolerant electrochemical energy storage. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 62. 7. L. Li, L. Xu, W. Ding, H. Lu, C. Zhang*, T. X. Liu*. Molecular-engineered hybrid carbon nanofillers for thermoplastic polyurethane nanocomposites with high mechanical strength and toughness. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2019, 177, 107381. 8. M. Liu, Y. Du, Y. Miao, Q. Ding, S. He, W. W. Tjiu, J. Pan, T. X. Liu*. Anisotropic conductive films based on highly aligned polyimide fibers containing hybrid materials of graphene nanoribbons and carbon nanotubes. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1037. 9. L. Jiang, C. Zhang, M. K. Liu, Z. Yang, W. W. Tjiu, T. X. Liu*. Simultaneous reinforcement and toughening of polyurethane composites with carbon nanotube/halloysite nanotube hybrids. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 91, 98. 10. Z. Yang, M. Liu, C. Zhang, W. W. Tjiu, T. X Liu*, H. Peng*. Carbon nanotubes bridged with graphene nanoribbons and their use in high-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3996. 11. M. Liu, C. Zhang, W. W. Tjiu, Z. Yang, W. Wang, T. X. Liu*. One-step hybridization of graphene nanoribbons with carbon nanotubes and its strong-yet-ductile thermoplastic polyurethane composites. Polymer 2013, 54, 3124. 12. M. Liu, Y. Miao, C. Zhang, W. W. Tjiu, Z. Yang, H. Peng, T. X. Liu*. Hierarchical composites of polyaniline-graphene nanoribbons-carbon nanotubes as electrode materials in all-solid-state supercapacitors. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7312. 13. C. Zhang, S. Huang, W. W. Tjiu, W. Fan, T. X. Liu*. Facile preparation of water-dispersible graphene sheets stabilized by acid-treated multi-walled carbon nanotubes and their poly(vinyl alcohol) composites. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 2427. 14. C. Zhang, W. W. Tjiu, W. Fan, Z. Yang, S. Huang, T. X. Liu*. Aqueous stabilization of graphene sheets using exfoliated montmorillonite nanoplatelets for multifunctional free-standing hybrid films via vacuum-assisted self-assembly. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 18011. 15. C. Zhang, W. W. Tjiu, T. X. Liu*, W. Y. Lui, I. Y. Phang, W.-D. Zhang*. Dramatically enhanced mechanical performance of nylon-6 magnetic composites with nanostructured hybrid one-dimensional carbon nanotube-two-dimensional clay nanoplatelet heterostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 3392. 16. C. Zhang, L. L. Ren, X. Y. Wang, T. X. Liu*. Graphene oxide-assisted dispersion of pristine multiwalled carbon nanotubes in aqueous media. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 11435. 17. S. Huang, H. D. Peng, W. W. Tjiu, Z. Yang, H. Zhu, T. Tang, T. X. Liu*. Assembling exfoliated layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanosheet/carbon nanotube (CNT) hybrids via electrostatic force and fabricating nylon nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 16766. 18. D. Chen, X. Wang, T. X. Liu*, X. Wang, J. Li. Electrically conductive poly(vinyl alcohol) hybrid films containing graphene and layered double hydroxide fabricated via layer-by-layer self-assembly. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2005. 19. S. Huang, X. Cen, H. Peng, S. Guo, W. Wang, T. X. Liu*. Heterogeneous ultrathin films of poly(vinyl alcohol)/layered double hydroxide and montmorillonite nanosheets via layer-by-layer assembly. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 15225. 20. W. D. Zhang*, I. Y. Phang, T. X. Liu*. Growth of carbon nanotubes on clay: Unique nanostructured filler for high-performance polymer nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 73.
|