Small - Tailoring the d‑Band Center of High-Entropy Perovskite Oxide Nanotubes for Enhanced Nitrate Electroreduction
Cun Chen#, Zhen Xu#, Guangtong Hai*, Wei-Hsiang Huang*, Chih-Wen Pao, Hanjun Li, Kezhu Jiang, Nan Zhang*, Tianxi Liu*
Small 2024, DOI: 10.1002/smll.202407964
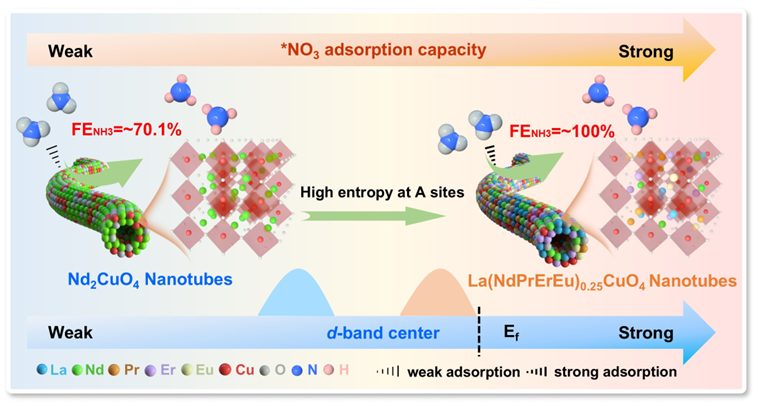
High-entropy perovskite oxides exhibit promising application prospects in the field of electrocatalysis, owing to their flexible elemental composition, plentiful active sites, and superior structural stability. Herein, high-entropy perovskite oxide nanotubes are prepared with La, Nd, Pr, Er, Eu at A-site by electrospinning as efficient electrocatalysts for nitrate reduction reaction (NO3RR). Electrochemical tests demonstrate that LaNd0.25Pr0.25Er0.25Eu0.25CuO4 nanotubes (LNPEEC NTs) display outstanding NO3RR performance, achieving a NH3 Faraday efficiency (FENH3) of 100% at −0.7 V versus reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) and a yield rateNH3 of 1378 µg h−1 mg−1cat. at −1.0 VRHE, outperforming Nd2CuO4 nanotubes (NC NTs). Furthermore, LNPEEC NTs also exhibit excellent stability even after 10 cycles at −0.7 VRHE and −1.0 VRHE. X-ray absorption spectroscopy confirms that multi-component regulation of A-site optimizes the coordination environment of Cu at B-site, increasing the unsaturated Cu sites and thus providing more active sites. Additionally, density functional theory calculations reveal that the doping of multi-component rare-earth elements at A-site in LNPEEC NTs modulates the d-band center of Cu at B-site and reduces the reaction energy barrier of the rate-determining step, thus enhancing the adsorption of NO3− and promoting the NO3RR performance.
Link: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202407964